(React) 클래스 컴포넌트의 라이프 사이클
목차
React 클래스 컴포넌트의 라이프 사이클
목차
요 며칠 자바스크립트와 리액트를 배우면서 리액트 클래스 컴포넌트의 생명주기에 대해서 배우게 되었다. 그렇게 생명주기에 대해 배우던중 componentWillUnmount() 내장 함수에대해 의문점이 생겼다.
컴포넌트 라이프 사이클
먼저 컴포넌트의 라이프 사이클이 어떻게 되는지 보겠다.

Unmount를 제외한 나머지는 컴포넌트 상태에때라 will과 did로 나뉜다.
Mount
-
componentWillMount
컴포넌트가 mount되기 전으로, 컴포넌트가 시작되면 context, props, state를 저장한 후 componentWillMount를 실행한다. 그후, 컴포넌트를 DOM에 부착한 후, componenteDidMount를 실행한다. 이 단계에서는 Mount 중이므로 props와 state를 바꾸면 안된다. DOM에도 접근하지 못한다고 한다. -
componentDidMount
DOM에 접근이 가능하다. 그래서 여기서는 주로 AJAX요청을 하거나 setInterval, setTimeout 같은 행동을 한다.
Update
Update는 Props Update와 State Update가 발생했을 때를 나눠서 보겠다.
-
Props Update
-
componentWillReceiveProps
업데이트가 되었음을 발견하고 componentWillReceiveProps 실행 -
shouldComponentUpdate
render 전 상황이므로 return false하면 render를 취소할 수 있다. 때문에 불필요한 업데이트를 걸러내는 성능 최적화를 이 단계에서 실행한다. -
componentWillUpdate
이 단계에서는 state를 바꾸면 안된다. -
componentDidUpdate
render 완료 후 실행. DOM접근 가능
-
-
State Update
Props Update와 다르게 componentWillReceiveProps 메소드를 호출하지 않는다.
* **shouldComponentUpdate**
* **componentWillUpdate**
* **componentDidUpdate**
Unmount
- componentWillUnmount
하나만 존재하며, 컴포넌트를 더는 사용하지 않을 때 호출한다. componentWillMount 연결했던 이벤트 리스너들을 해제해주는 등의 활동을 한다.
예제에서의 의문점
의문이 생긴 예제를 보겠다. 예제는 정해진 시간마다 NotificationList를 출력하는 예제이다. 여기에 component 라이프사이클을 확인하는 콘솔 출력문을 추가해줬다.
import React from "react";
import Notification from "./Notification";
const reservedNotifications = [
{
id:1,
message: "안녕하세요, 오늘 일정을 알려드립니다.",
},
{
id:2,
message: "점심 식사 시간입니다.",
},
{
id:3,
message: "풋살 할 시간입니다..",
}
];
var timer;
class NotificationList extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = {
notifications: []
};
}
componentDidMount(){
const {notifications} = this.state;
timer = setInterval(() => {
if(notifications.length < reservedNotifications.length){
const index = notifications.length;
notifications.push(reservedNotifications[index]);
this.setState({
notifications: notifications
});
} else {
this.setState({
notifications: []
});
clearInterval(timer);
}
}, 3000)
}
componentWillUnmount(){
if(timer){
clearInterval(timer)
}
}
render(){
return (
<div>
{this.state.notifications.map((notification) => {
return <Notification key={notification.id} id={notification.id} message={notification.message}/>
})}
</div>
);
}
}
export default NotificationList;
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
import './index.css';
import reportWebVitals from './reportWebVitals';
import NotificationList from './chapter_04/NotificationList';
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<NotificationList/>
</React.StrictMode>
);
// If you want to start measuring performance in your app, pass a function
// to log results (for example: reportWebVitals(console.log))
// or send to an analytics endpoint. Learn more: https://bit.ly/CRA-vitals
reportWebVitals();
위 파일들을 만들고 실행해 보면
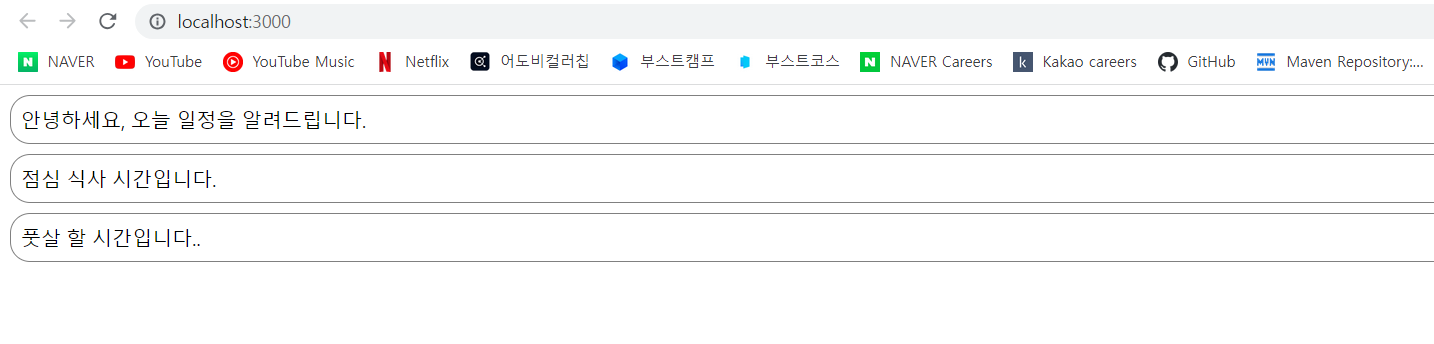
3초 마다 하나씩 할일이 뜬다.
그리고 콘솔창을 확인해보면
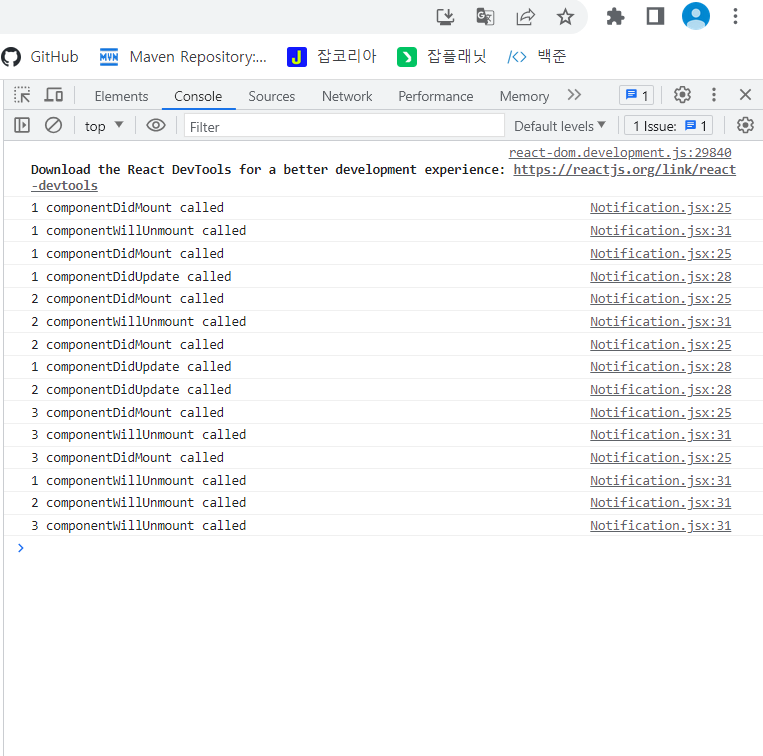
이런식으로 상태가 뜬다.
여기서 의문이 들었는데,
componentDidMount() 는 컴포넌트가 생성되고 난 후 생성되는 매서드이고,
componentDidUpdate() 는 컴포넌트에 변경점이 생겼을때,
componentWillUnmount() 는 컴포넌트가 생명주기를 다해 제거될 때 생성된다고 한다.
그렇다면 콘솔 창에서는 (componentDidMount() -> componentDidUPdate())3 -> componentWillUnmount()3 이런식으로 떠야하는 것이 아닐까? 마지막에 몰아서 Unmount 떠야한다고 생각했지만 콘솔창에는 Unmount가 세번 뜨기 전에도 몇번씩 뜨는걸 확인 할 수 있다.
코드의 문제인지, 내가 모르는 라이프 사이클이 과정이 있는지 알아봐야겠다.
추가
이유를 알았다. componentWillUnmount() 매서드는 없어지면서 실행되는 매서드가 아니라 없어지기전에 실행되는 매서드라는 점이 포인트다. 그래서 콘솔창에 중간중간 unmount가 찍히는 것은 곧 없어질 컴포넌트지만 그 뒤 다시 생성 및 업데이트가 되면서 생명주기가 처음으로 돌아가기 때문이다.
그래서 componentWillUnmount()가 실행되지만 컴포넌트가 사라지기전에 다시 생명주기를 처음으로 되돌리는 것이다.